Labs and Lytes 023
Author: Chris Sia
Reviewers: Sarah Yong and Chris Nickson
A 60-year old gentleman presents with long standing dyspnea and cyanosis.
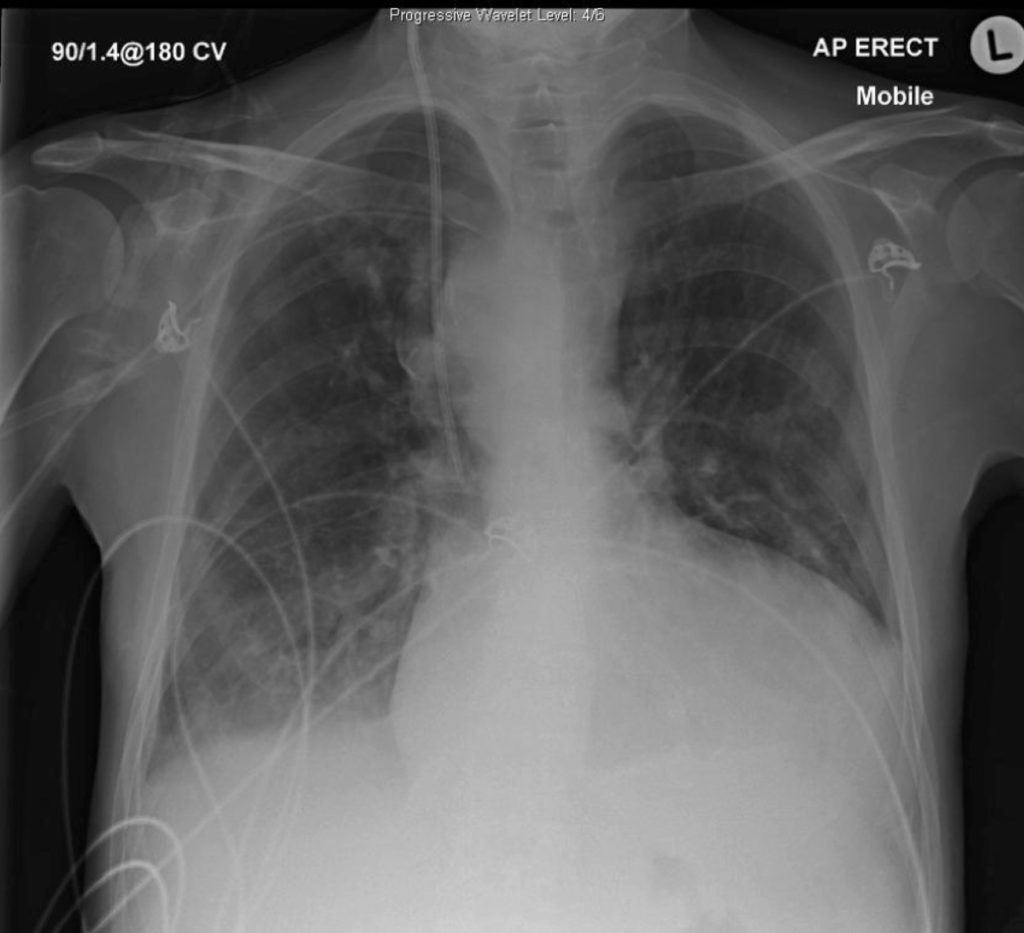
This is his chest x-ray:
Q1. Describe the x-ray findings?
This is an AP Erect chest x-ray. The most striking finding is the boot-shaped heart, in this case due to Tetralogy of Fallot.
Other features of this CXR:
- Tracheal deviation to the left, pushed by mediastinal mass
- Right lower zone alveolar opacity
- Right internal jugular central line, tip appropriately within SVC
- Right PICC
- ECG leads
Q2. What are the differentials for an anterior mediastinal mass?
The 5Ts mnemonic is useful here:
- Thymus: thymoma, thymic carcinoma
- Thyroid: goitre, thyroid carcinoma, parathyroid neoplasms
- Teratoma and other germ cell tumours
- Thoracic aortic aneurysm (or other aortic abnormality!)
- Terrible lymphoma: Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin
Q3. What is the likely cause of the mediastinal mass in this CXR?
Right sided aortic arch (this is seen in 25% of cases of TOF)
Q4. What are the 4 features of Tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of Fallot is a constellation of the following four cardiac abnormalities, arising from a single developmental defect:
- Ventricular septal defect
- Overriding aorta
- Right ventricular outflow tract obstruction
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
TOF accounts for 10% of congenital heart disease